Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasoundNuclear Medicine
Imaging ITIndustry News
Events

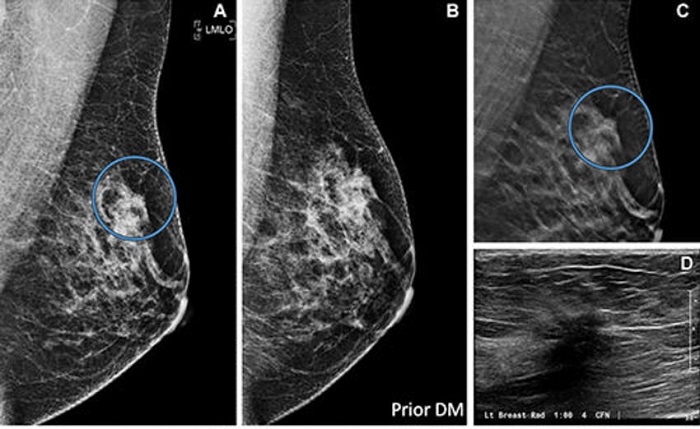
- Advanced 3D Mammography Detects More Breast Cancers
- AI X-Ray Diagnostic Tool Offers Rapid Pediatric Fracture Detection
- AI-Powered Chest X-Ray Analysis Shows Promise in Clinical Practice
- AI-Based Algorithm Improves Accuracy of Breast Cancer Diagnoses
- Groundbreaking X-Ray Imaging Technique Could Improve Medical Diagnostics
- AI Algorithm Analyzes MRI Scans to Determine Best Rectal Cancer Treatment Strategy
- AI Software Uses MRI Scans to Automatically Segment Key Brain Structures for Improved Radiation Therapy Planning
- AI Software Analyzes Neuroimaging Data and Patient Information to Diagnose 10 Types of Dementia
- Metamaterials to Make MRI Scans Faster, Cheaper, and More Accurate
- Deep Learning Enables Accurate, Automated Quality Control Image Assessment for Liver MR Elastography
- Radiology Test Non-Invasively Diagnoses Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Associated AKI
- New PET/CT Technique Accurately Detects Neuroblastoma in Children with Short Scan Time and No Anesthesia
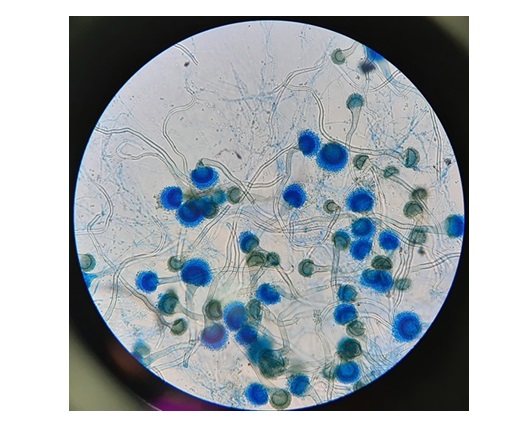
- New Imaging Method Enables Early Detection of Fungal Infections Caused by Aspergillus Fumigatus
- New Imaging Method Non-Invasively Detects Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- FAPI PET/CT Improves Staging of Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer
- Ultrasound Test Detects Ovarian Cancer in Postmenopausal Women with Highest Accuracy Of 96%
- Ultrasound-Activated Hydrogel Could Revolutionize Drug Delivery for Medical Applications
- Wearable Ultrasound Navigation System Could Improve Lumbar Puncture Accuracy
- New Ultrasound Technologies Improve Diagnosis for Cancer, Liver Disease and Other Pathologies
- Wearable Ultrasound Device Helps Hospital Reduce Sepsis Mortality, Length of Stay, and Cost
- AI Algorithm Reduces Unnecessary Radiation Exposure in Traumatic Neuroradiological CT Scans
- New Solution Enhances AI-Based Quality Control and Diagnosis in Medical Imaging
- AI Tool Detects Cervical Spine Fractures from CT Scans
- Flat Panel Detector Speeds Up Imaging and Diagnosis
- AI Tool Accurately Predicts Stroke Outcomes After Arterial Clot Removal Using CTA Scans
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Innovative Collaboration to Enhance Ischemic Stroke Detection and Elevate Standards in Diagnostic Imaging
- RSNA 2024 Registration Opens
- Microsoft collaborates with Leading Academic Medical Systems to Advance AI in Medical Imaging
- GE HealthCare Acquires Intelligent Ultrasound Group’s Clinical Artificial Intelligence Business
- Bayer and Rad AI Collaborate on Expanding Use of Cutting Edge AI Radiology Operational Solutions

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasoundNuclear Medicine
Imaging ITIndustry News
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasoundNuclear Medicine
Imaging ITIndustry News
Events
Advertise with Us


- Advanced 3D Mammography Detects More Breast Cancers
- AI X-Ray Diagnostic Tool Offers Rapid Pediatric Fracture Detection
- AI-Powered Chest X-Ray Analysis Shows Promise in Clinical Practice
- AI-Based Algorithm Improves Accuracy of Breast Cancer Diagnoses
- Groundbreaking X-Ray Imaging Technique Could Improve Medical Diagnostics
- AI Algorithm Analyzes MRI Scans to Determine Best Rectal Cancer Treatment Strategy
- AI Software Uses MRI Scans to Automatically Segment Key Brain Structures for Improved Radiation Therapy Planning
- AI Software Analyzes Neuroimaging Data and Patient Information to Diagnose 10 Types of Dementia
- Metamaterials to Make MRI Scans Faster, Cheaper, and More Accurate
- Deep Learning Enables Accurate, Automated Quality Control Image Assessment for Liver MR Elastography
- Radiology Test Non-Invasively Diagnoses Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Associated AKI
- New PET/CT Technique Accurately Detects Neuroblastoma in Children with Short Scan Time and No Anesthesia
- New Imaging Method Enables Early Detection of Fungal Infections Caused by Aspergillus Fumigatus
- New Imaging Method Non-Invasively Detects Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- FAPI PET/CT Improves Staging of Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer
- Ultrasound Test Detects Ovarian Cancer in Postmenopausal Women with Highest Accuracy Of 96%
- Ultrasound-Activated Hydrogel Could Revolutionize Drug Delivery for Medical Applications
- Wearable Ultrasound Navigation System Could Improve Lumbar Puncture Accuracy
- New Ultrasound Technologies Improve Diagnosis for Cancer, Liver Disease and Other Pathologies
- Wearable Ultrasound Device Helps Hospital Reduce Sepsis Mortality, Length of Stay, and Cost
- AI Algorithm Reduces Unnecessary Radiation Exposure in Traumatic Neuroradiological CT Scans
- New Solution Enhances AI-Based Quality Control and Diagnosis in Medical Imaging
- AI Tool Detects Cervical Spine Fractures from CT Scans
- Flat Panel Detector Speeds Up Imaging and Diagnosis
- AI Tool Accurately Predicts Stroke Outcomes After Arterial Clot Removal Using CTA Scans
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Innovative Collaboration to Enhance Ischemic Stroke Detection and Elevate Standards in Diagnostic Imaging
- RSNA 2024 Registration Opens
- Microsoft collaborates with Leading Academic Medical Systems to Advance AI in Medical Imaging
- GE HealthCare Acquires Intelligent Ultrasound Group’s Clinical Artificial Intelligence Business
- Bayer and Rad AI Collaborate on Expanding Use of Cutting Edge AI Radiology Operational Solutions








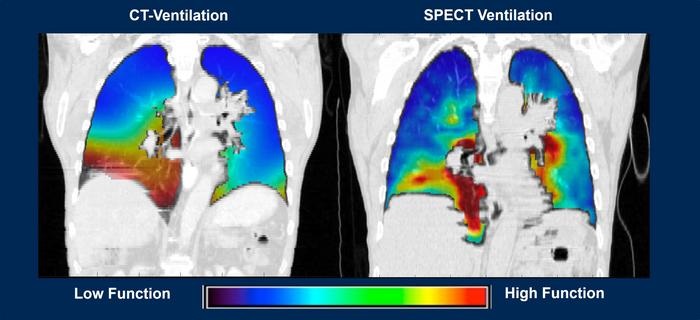











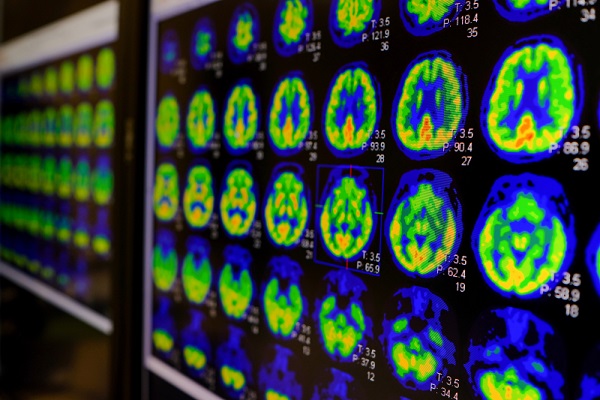
![Image: [18F]MFBG LAFOV PET/ULD CT (top) and [123I]MIBG scintigraphy with SPECT/LD CT images (bottom) of 7-wk-old girl with neuroblastoma (Photo courtesy of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine) Image: [18F]MFBG LAFOV PET/ULD CT (top) and [123I]MIBG scintigraphy with SPECT/LD CT images (bottom) of 7-wk-old girl with neuroblastoma (Photo courtesy of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine)](https://globetechcdn.com/medicalimaging/images/stories/articles/article_images/2024-08-22/JNM Aug 2024 - Borgwardt Figure 3A.jpg)